Fermented foods are an excellent source of probiotics and can help improve gut bacteria, providing essential bacterial cultures necessary for digestive health and immune functioning.
Fermented foods were an integral part of our ancestors’ daily diet as a means to preserve food without refrigeration, keeping fresh produce such as vegetables, fruit, and meats available and preserved.
Fermentation involves yeast or bacteria converting sugars and starches into organic acids (such as lactic acid) or alcohol for consumption by living organisms, similar to what happens when cheese, pickles and yogurts are aged.
Yogurt and kefir are among the most accessible fermented foods packed with probiotics, making them great tools to increase gut microbiome health and combat digestive issues, boost immunity, and reduce stomach issues such as gas, bloat, cramping, and IBS symptoms.
To learn more about fermented foods and their effect on gut bacteria, continue reading.
1. What Is Gut Bacteria?
Your gut microbiome is the collection of bacteria and other microbes living within your digestive tract that contribute to your overall health, such as digestion of food, regulation of immune function, and helping you feel good.
Your gut bacteria have an immense effect on your health from birth and throughout your lifetime, controlling how food digests in your stomach, immune function, and even brain health.
There are various strategies you can employ to ensure the well-being of your gut bacteria, such as increasing its count by eating plenty of vegetables and fruit.
Consuming fermented foods such as yogurt and kimchi also have a positive effect on your gut microbiome.
If you’re suffering from IBS symptoms, such as constipation or diarrhea, you may consider taking additional supplements that will ease these symptoms. If you wish to learn more, read the article here.
2. What Exactly Are Fermented Foods, and How Are They Beneficial?
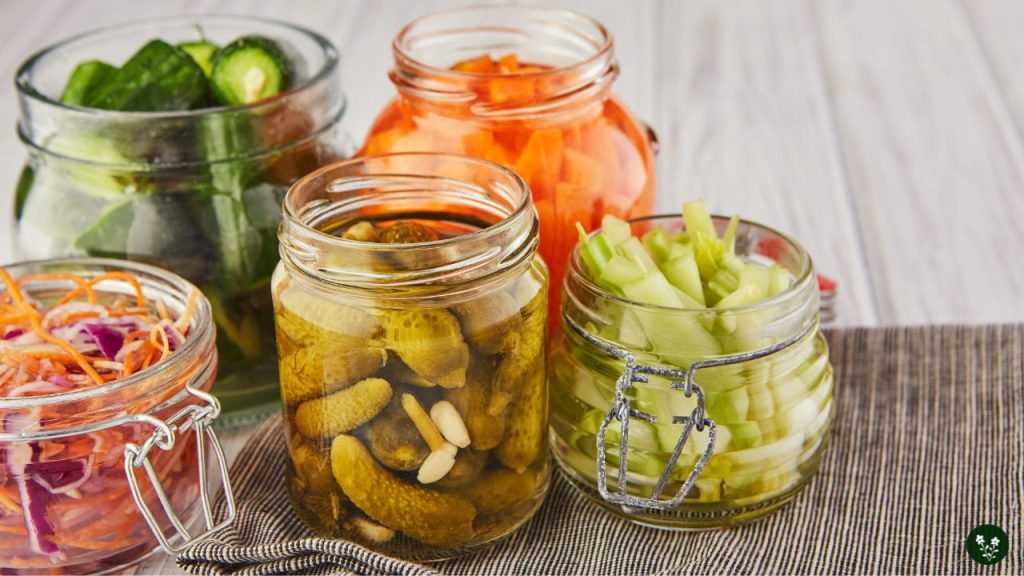

Fermentation refers to the process of turning foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy products, into something entirely new by adding bacteria or yeast to them.
Fermented foods have been around since ancient times but have recently seen increased interest due to potential health benefits.
Fermented foods containing probiotics are beneficial in aiding digestion and relieving symptoms associated with digestive disorders like IBS or candida gut, which may cause inflammation.
These foods can also help fight infections by providing essential bacteria with antioxidant benefits.
Yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut are among the most beloved fermented foods, but there’s so much more available besides.
Check stores or farmers markets near you, or make them yourself at home using a yogurt starter culture, kombucha tea, and pickling brine.
3. How Fermented Foods Improve Your Gut and Overall Health?
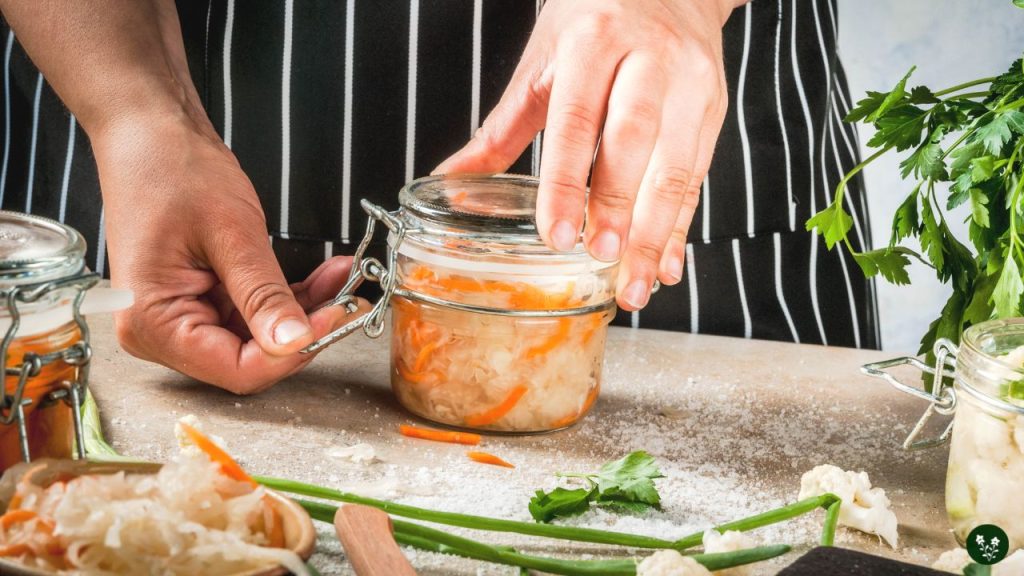

Fermented foods are great ways to improve gut health by maintaining a balance of healthy bacteria in the stomach, strengthening immunity, and decreasing inflammation symptoms.
Your gut is your body’s first line of defense against illness, so ensuring its optimal condition is critical to overall wellness.
When bacteria levels in your stomach become disturbed, they weaken immunity and increase the chances of flu or other infections taking hold in your system.
Fermented foods provide probiotics that replenish the beneficial bacteria in your stomach, improving immunity and alleviating inflammation symptoms.
They also boost the production of digestive enzymes that allow your body to process food more efficiently, leading to less bloating and constipation.
Fermented foods contain anti-inflammatory properties that may lower your risk for cardiovascular disease, cancer, arthritis, and other inflammatory illnesses.
Furthermore, fermented foods are high in antioxidants essential for combatting oxidative stress.
Research has demonstrated the link between probiotics and reduced inflammation, and improved sleep quality.
Live bacteria present in fermented foods are thought to support neurotransmitter production, helping alleviate anxiety and depression symptoms.
4. Using Fermented Foods to Boost Your Gut Bacteria
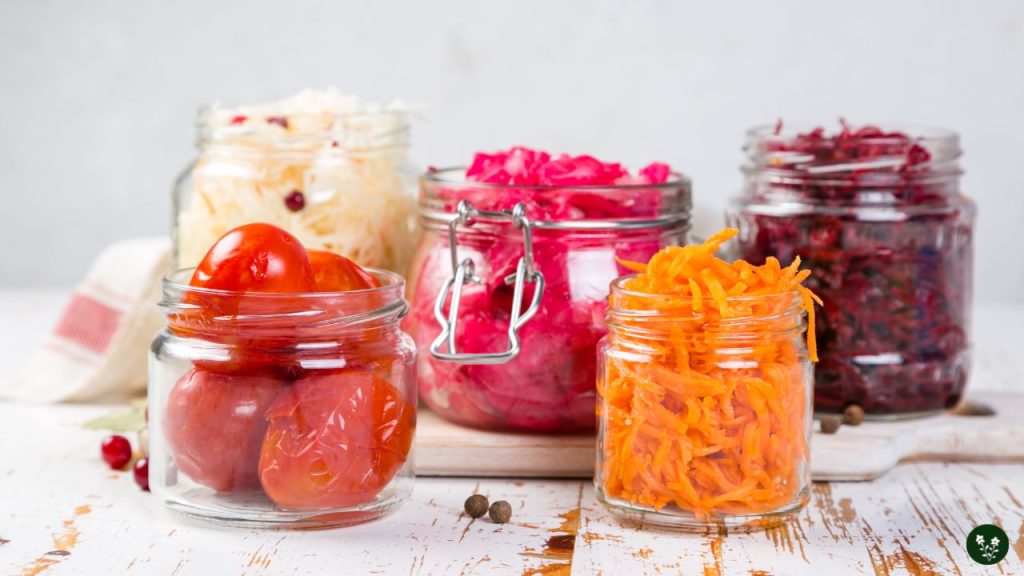

Integrating fermented foods into your diet isn’t only about taste.
These probiotic-rich foods are also good for your health, supporting digestive wellness and helping maintain weight management by strengthening gut bacteria.
Read on to discover how you can include these delicious yet nutritional products in your meal plans.
Add Sauerkraut to Sandwiches and Salads
Sauerkraut is an easy and accessible way to add more fermented foods into your diet, available at most grocery stores as well as being made at home quickly.
Sauerkraut is an integral component of many dishes, featuring its signature tart and zesty flavor in salads and sandwiches alike.
To create a simple salad, just combine drained sauerkraut with chopped green peppers, celery, and onions in a large bowl.
Drizzle on some white vinegar and a dash of sugar before stirring in your dressing of choice.
Snack on Yogurt With Live Cultures
You can produce yogurt by adding bacteria to milk in order to promote fermentation.
Once fermented, these microbes metabolize lactose from the milk into lactic acid that binds with other molecules to create its signature thick consistency – creating delicious yogurt-flavored treats.
Yogurt contains microbes that support digestion by maintaining a healthy balance of “good” bacteria in the gut.
You can buy yogurt from the store or make it at home by adding different flavors to it.
Top a Stir-Fry With Kimchi
Kimchi is an ideal way to increase your probiotic intake. Plus, its versatility means you can use it in many recipes.
If you have extra kimchi on hand, add it to a stir-fry. Its spicy bite will bring additional layers of flavor. To create the stir-fry, heat oil in a wok or large skillet over medium-high heat and add onions.
After three minutes have passed, stir constantly so they soften completely.
Remove vegetables to one side of the pan, add kimchi and cooked noodles, then stir well to mix and serve immediately.
Add Kefir to Smoothies
If you’re looking for an easy way to add more fermented foods to your diet, add Kefir to smoothies. Kefir is a tasty source of probiotics and may help reset your gut microbiome.
Helping improve bone health, reduce blood sugar levels, regulate your immune system, and more. You can easily produce kefir at home using kefir grains and high-quality milk.
Simply mix the two together, allow it to sit for 24 hours, and strain out your finished product.
Make Salad Dressings Out of Miso Paste
Miso is a Japanese condiment that you can make from fermented soybeans, salt, and koji (a form of fungus).
You can use it in many dishes, from dressings to soups. You can make a quick and easy miso salad dressing using just two steps.
Combine ingredients in either a food processor or whisk by hand to produce a creamy and savory sauce. Then add it to any bowl of salad.
5. Other Fermented Foods You Can Add to Your Diet

Here are some other fermented foods you can add to your diet for more benefits:
- Fermented Cottage Cheese
- Buttermilk
- Kombucha
- Aged Cheese
- Pickled Vegetables
- Tempeh
- Natto
- Vegetable Brine
Conclusion
Your gut serves as the second brain of your body, impacting everything from mood and appetite regulation to immune function and immunity.
By eating fermented foods regularly, you can increase the number of beneficial bacteria found within the “gut biome.”
Moreover, improving its ability to digest food efficiently while also helping your entire system work more smoothly.
Furthermore, fermented foods can also help to reduce inflammation as well as boost immune and brain function.



